
Types of Rubber Products-SKYRUB
Rubber Products are diverse in type and classification. If categorized by application, they can be summarized into the following six major categories, with the structural characteristics, application scenarios, and industry status of each category as follows:

Introduction to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPM, EPDM) -SKYRUB
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is a rubber synthesized by solution copolymerization of ethylene ( CH2=CH2 ) and propylene ( CH2=CH-CH2 ), known as binary ethylene propylene rubber ( EPM ).
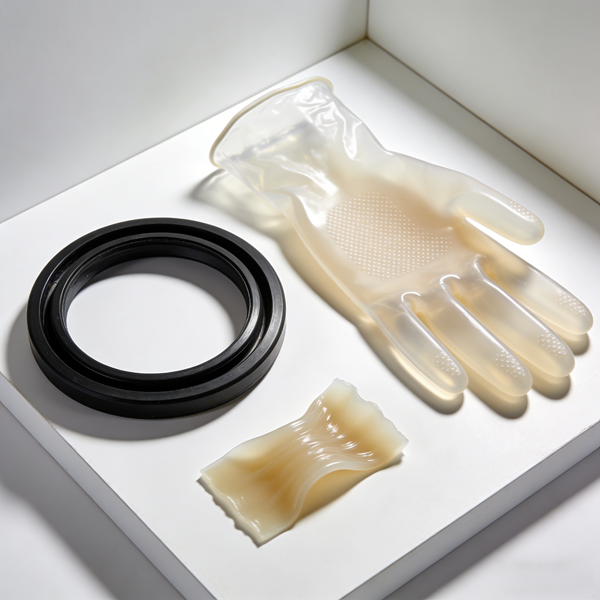
Introduction to Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) -SKYRUB
Molded liquid silicone rubber ( LSR ) is a high-performance type of silicone rubber. Compared to condensation-type silicone rubber, it produces fewer byproducts during vulcanization, has less shrinkage, can be vulcanized more deeply, and exhibits better high-temperature performance. Furthermore, the LSR process is simple and inexpensive.

Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) -SKYRUB
Because of the presence of double bonds in the main chain of NBR , its weather resistance, heat resistance, and chemical stability are poor, which limits its application range.
Rubber Processing Technology - SKYRUB
Rubber processing involves multiple core procedures, each with significantly different operational objectives, processes, and safety risks. The following details the core content and safety points of each procedure in the order of the process flow:
Introduction to Natural Rubber - SKY RUBBER
Natural rubber refers to rubber obtained from plants. There are about 200 kinds of plants on Earth that can biosynthesize rubber, the main one being the Brazilian rubber tree, followed by silver chrysanthemum, rubber grass, eucommia, etc.
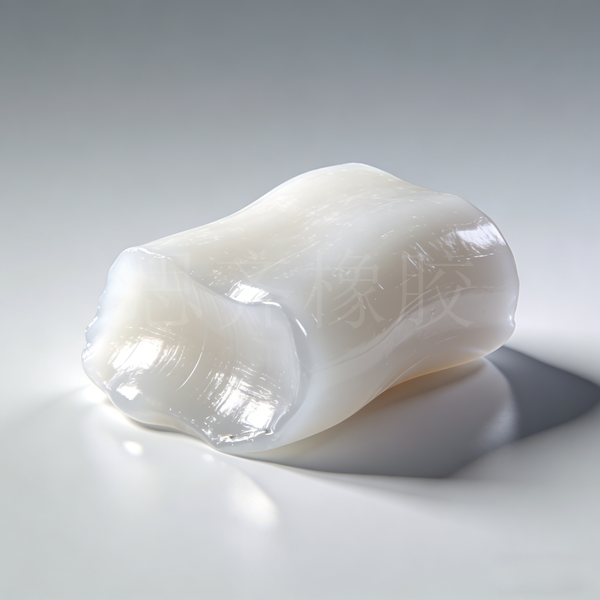

Introduction to Butadiene Rubber (BR) -SKY RUBBER
Butadiene rubber, short for cis -1,4- polybutadiene rubber, has the molecular formula (C4H6)n . It is a structurally regular synthetic rubber polymerized from butadiene, with a cis structure content exceeding 95% .
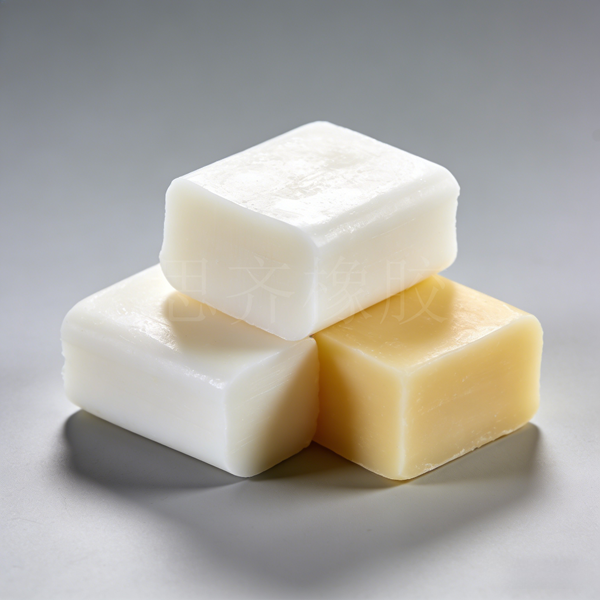

Introduction to Chloroprene Rubber (CR) -SKY RUBBER
Chloroprene rubber is an elastomer made from chloroprene monomers through emulsion polymerization, coagulation, and drying. It was industrialized in 1931 , initially produced by DuPont in the United States. Global annual production is currently approximately 2 million tons.
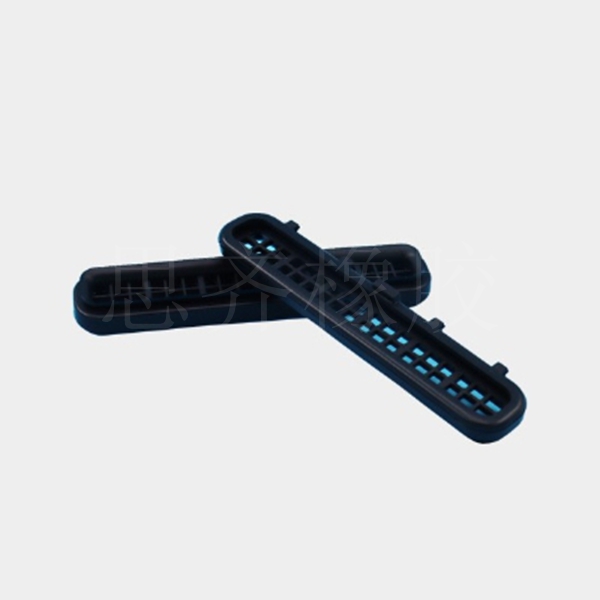

Introduction to Fluororubber (FPM, FKM) -SKY RUBBER
Fluororubber refers to a group of elastomers whose molecular chains contain fluorine-containing side groups. There are 10 types, among which copolymers of vinylidene fluoride and perfluoropropylene, or with the addition of tetrafluoroethylene, are commonly used. In China, this type of rubber is called type 26 fluororubber, while DuPont calls it Viton -type fluororubber.
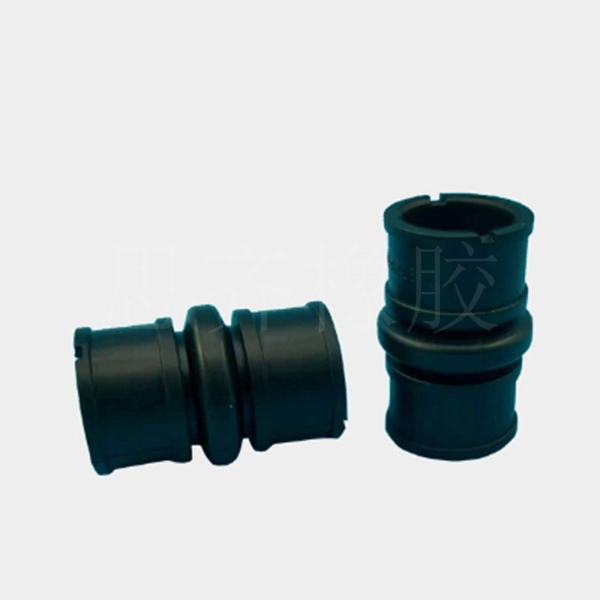

Introduction to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) -SKY RUBBER
butadiene rubber (NBR) is a polymer formed by emulsion copolymerization of butadiene ( CH2=CH-CH=CH2 ) and acrylonitrile ( CH2=CH-CH-CN ), with an average molecular weight of around 700,000 . Rubber polymerized at 25 ℃ -50 ℃is called thermopolymerized NBR. NBR is renowned for its excellent oil resistance. Among existing rubbers, its oil resistance is second only to polysulfide rubber, acrylate rubber, and fluororubber, making it widely used in the Rubber Industry.


