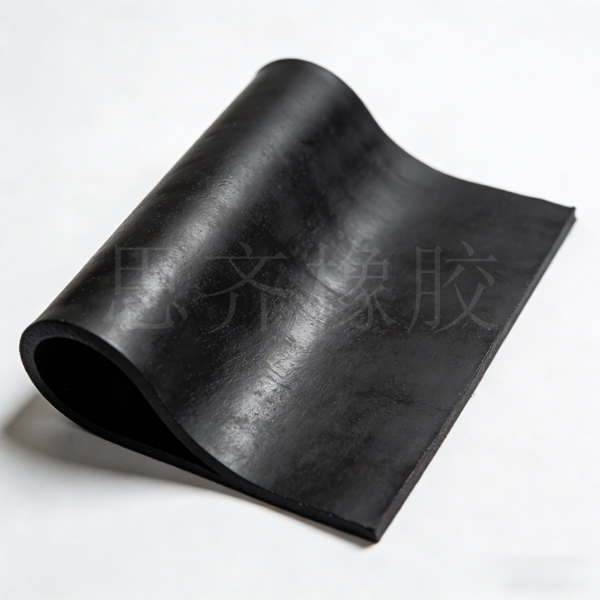
Introduction to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPM, EPDM) -SKYRUB
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is a rubber synthesized by solution copolymerization of ethylene ( CH2=CH2 ) and propylene ( CH2=CH-CH2 ), known as binary ethylene propylene rubber ( EPM ). Its molecular chain does not contain double bonds, making it difficult to vulcanize. To improve its vulcanization and crosslinking properties , a third monomer containing double bonds is introduced. EPM with the third monomer is called ternary ethylene propylene rubber ( EPDM ), with an average molecular weight of over 250,000 .
Binary ethylene propylene rubber is a saturated elastomer, meaning its molecular chain does not contain double bonds and cannot be vulcanized with sulfur, but it can be vulcanized with peroxide ( DCP). Because ternary ethylene propylene rubber contains a smaller amount of the third monomer, its properties are not significantly different from those of binary ethylene propylene rubber.

Performance characteristics :
Advantages: Non-polar, high insulation, ozone resistance, UV resistance, excellent weather resistance and heat aging resistance, ranking first among general-purpose rubbers, acid and alkali resistance, low specific gravity, and can be compounded with high fillers.
Disadvantages: Poor resistance to non-polar oils and solvents, poor adhesion to other materials, and slower vulcanization rate than other diene rubbers.
Operating temperature range: approximately -40 to +150 ℃.
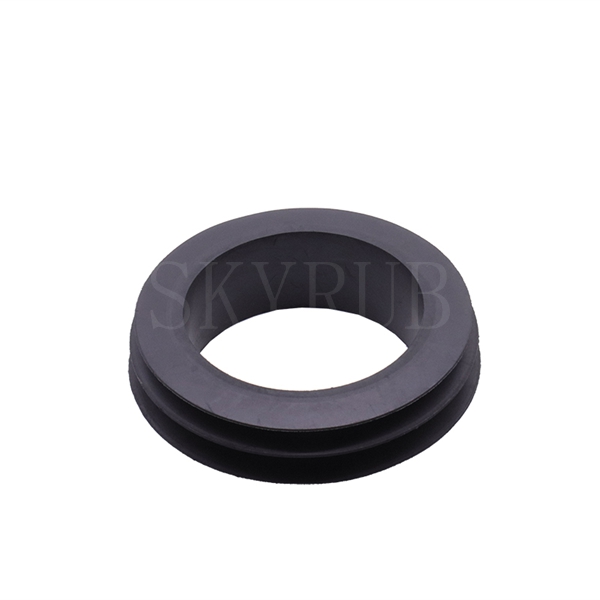
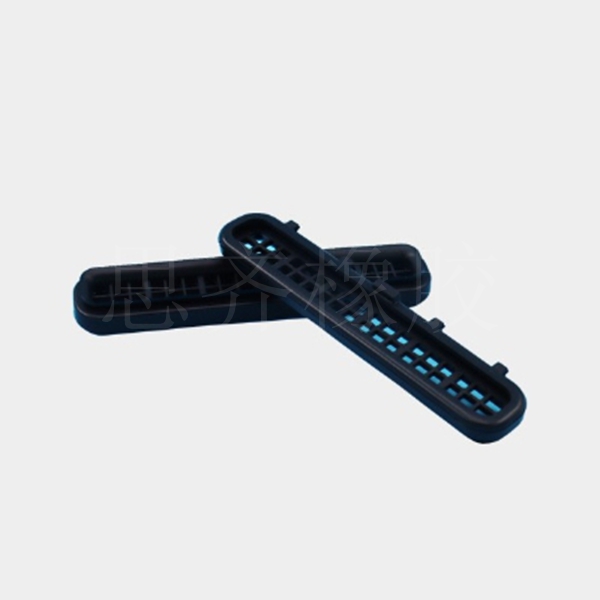
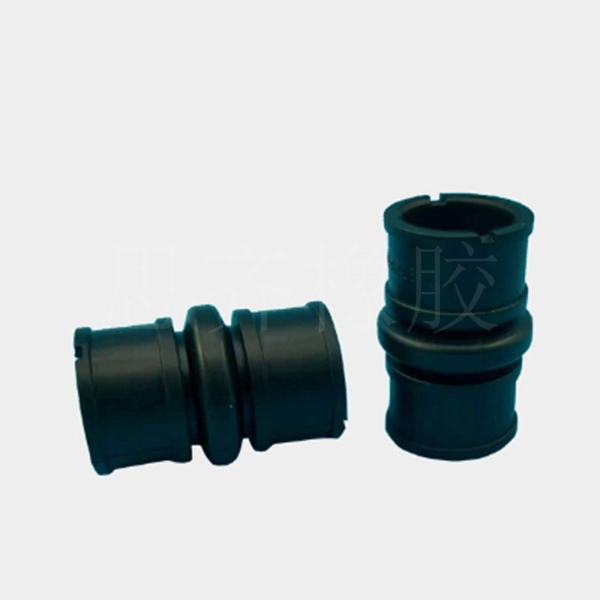
Main applications : Widely used in automotive parts, waterproof building materials, wire and cable sheaths, heat-resistant hoses, tapes, Automotive Seals, lubricant additives and other products.