Types of Rubber Products-SKYRUB
Rubber Products are diverse in type and classification. If categorized by application, they can be summarized into the following six major categories, with the structural characteristics, application scenarios, and industry status of each category as follows:
- Tires: The core category of rubber products
Tires are the largest application of rubber, with 50% to 60% of global rubber resources used in tire production. Rubber can be categorized based on two dimensions: "application" and "structure."
According to their uses: they cover automobile tires, aircraft tires, tractor tires, construction machinery tires, etc., each adapted to different load, speed and working conditions.
Tires can be classified by structure into solid tires and pneumatic tires. Solid tires are only used for short-distance transportation on cranes and electric vehicles; hollow pneumatic tires are used on automobiles, airplanes, tractors, and various construction machinery vehicles.
- Bicycle tires: Essential goods for people's livelihood and industry and agriculture
Handcart tires primarily serve short-distance commuting and light transportation. The core categories include handcart tires and bicycle tires, which can be further divided according to structural differences:
Soft-side tires and hard-side tires: Due to differences in tire body structure design, there are slight differences in the molding process between the two.
- Conveyor Belts: Core Components of Industrial Power and Conveying
Adhesive tapes can be clearly divided into two main categories based on their function: "conveyor belts" and "transmission belts," each with its own specific role in industrial settings.
Conveyor belt: It is the core component of belt conveyor and is widely used in metallurgy, coal, chemical, construction and other industrial fields, as well as transportation industry, to undertake the task of long-distance transportation of granular and lumpy materials.
Transmission belts: With power transmission as their core function, they include flat transmission belts, V-belts, synchronous toothed belts, continuously variable belts, and high-speed ring belts. Their advantages lie in smooth and noiseless operation, ability to buffer heavy load impacts, and ease of manufacturing and installation, making them the mainstream transmission device for various mechanical equipment (such as machine tools and motors).
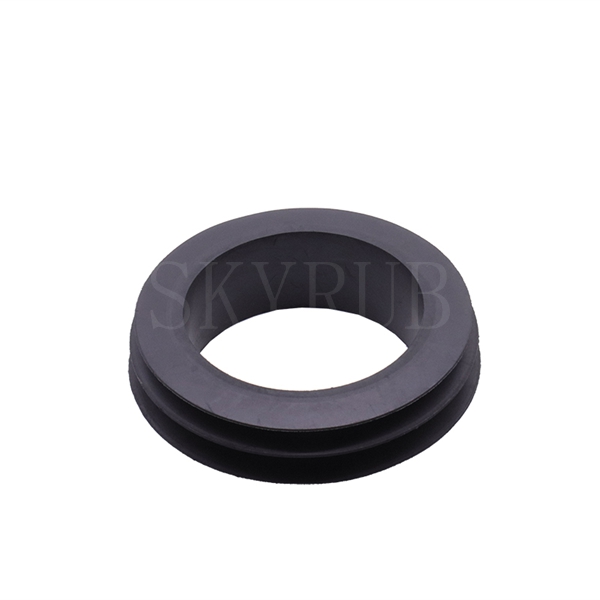

- Rubber Hoses: Specialized components for fluid and material transportation
The core function of rubber hoses is to transport liquids, gases, or granular solid materials. They can be classified in two ways: "function-oriented" and "production-oriented."
Based on function, hoses are divided into pressure-resistant hoses, suction hoses, and pressure-resistant/suction dual-purpose hoses, corresponding to different conveying scenarios with varying pressure and suction requirements.
Based on materials and structure (commonly used by enterprises): there are six types of hoses: all-rubber hoses, fabric-reinforced hoses, braided hoses, spiral hoses, knitted hoses, and suction hoses. Different structural designs determine the pressure resistance, flexibility, and applicable media range of the hoses.
- Rubber Shoes: Daily Necessities Suitable for Multiple Scenarios
Rubber shoes combine everyday wear with professional protective features, and their classification logic is clear:
Based on structural characteristics, shoes can be mainly divided into rubber-soled shoes (fully covered in rubber, highly waterproof) and cloth-soled shoes (cloth upper combined with rubber sole, excellent breathability).
According to the intended user, shoes can be categorized as follows: military shoes (wear-resistant and puncture-resistant), mining shoes (impact-resistant and slip-resistant), agricultural and forestry work shoes (corrosion-resistant and mud-resistant), general wear shoes (daily leisure), and sports shoes (lightweight and shock-absorbing).
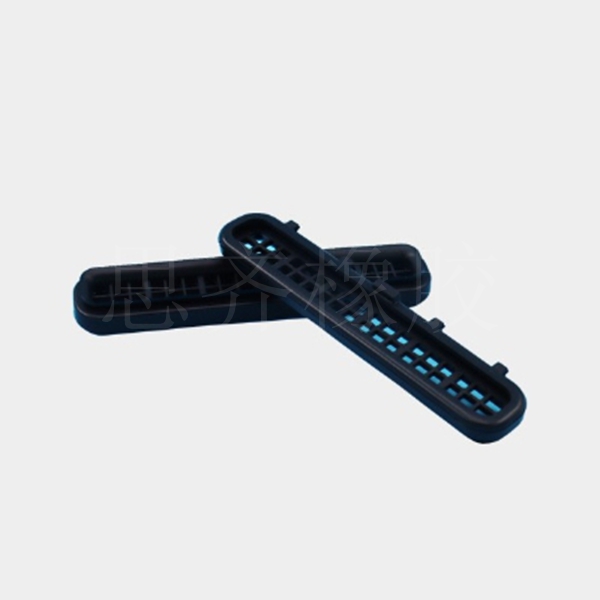
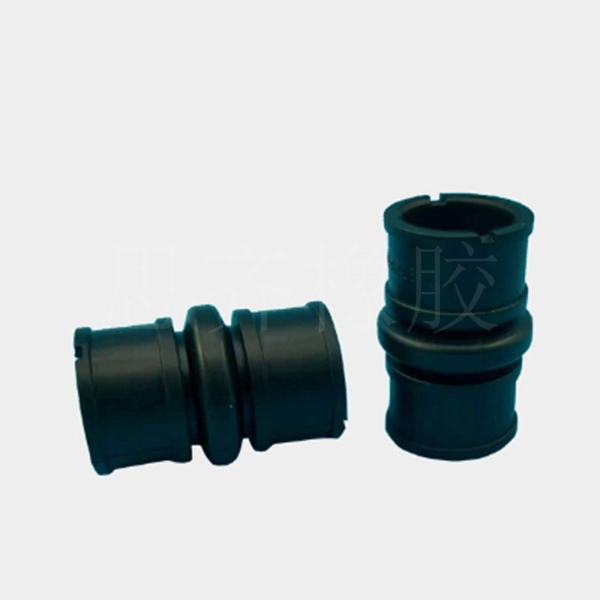
- Industrial Rubber Products: Diversified "Miscellaneous" Category
In addition to the five core product categories mentioned above, rubber is also widely used in various industrial special-purpose parts. Because these products are diverse and their individual product categories are smaller than those of tires, they are commonly referred to in the industry as rubber "miscellaneous products," which mainly include:
According to function, rubber Seals, rubber shock absorbers, and rubber protective components are classified as follows:
According to industry: rubber parts for automobiles, silicone parts for medical devices, rubber parts for home appliances, rubber parts for consumer electronics, rubber parts for baby products, rubber parts for household goods, rubber parts for motor equipment, etc.